This story first appeared in the US in the September/October 2024 issue of Hagerty Drivers Club magazine. It explores the developmental timeline of horsepower in the automotive industry. We kicked things off with the engine’s early development, from 1776–1900, here. Time marched on, and so did our coverage, through the early 20th century, the 1920s–40s, and the 1950s. Stay tuned as we continue our daily installments highlighting all the major evolutionary milestones in horsepower. Enjoy! –Ed.
How much horsepower does it make? The question is, in many practical respects, pointless. Pretty much every vehicle on the road has enough power to do what it needs to do, and then some. Yet for enthusiasts, it’s critical, part of a secret handshake that tells us not only what someone’s driving, but whether they know and appreciate what they’re driving.

The horsepower your car produces is the product of some 250 years of continuous improvement, serendipitous discoveries, and daring feats – most of it revolving around a type of air pump we call the internal combustion engine.
As we write this, the future of the engine, the beating heart of the automobile, is somewhat in doubt. There’s no question, though, that our horsepower quest will continue. We will keep tweaking, and the numbers will keep growing. But it’s worth pausing, if only for a moment, to reflect on just how far we’ve come.
***

1962: General Motors adds turbochargers to Chevy Corvair Monzas and Oldsmobile Jetfires, yielding 150 horsepower and 215 horsepower, respectively. The benefit of turbocharging is using normally wasted exhaust energy to pack additional air into the engine, under pressure. BMW followed suit a decade later with the 2002 Turbo providing 170 horsepower from 2.0 litres; the 1975 Porsche 911 Turbo 3.0 brought 260 horsepower. In 1978, Buick rejoined the turbo club with its Regal Sport Coupe powered by a 150bhp, 3.8-litre V6.
Retired racer Carroll Shelby creates his first Cobra by cramming 271bhp small-block Ford V8s into Ace roadster bodies supplied by AC.
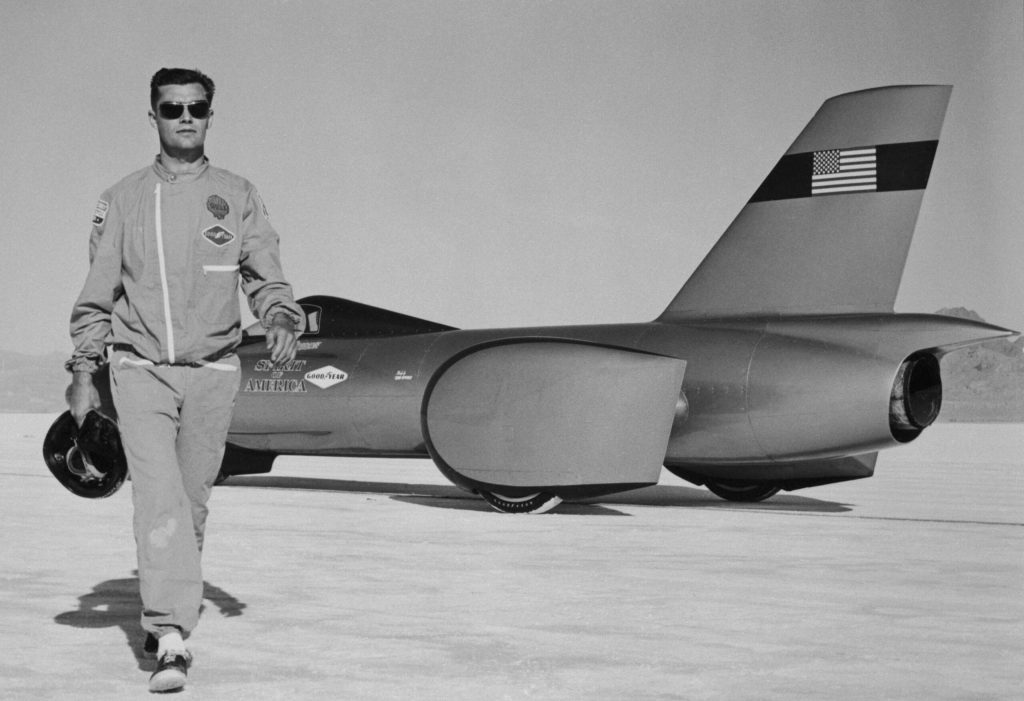

1963: Craig Breedlove is the first to top 400mph, driving Spirit of America, which is essentially a wingless airplane. Power comes from a General Electric J47 turbojet engine from an F-86 aircraft. Breedlove tops 500mph a year later, then 600mph in ’65. His wife Lee topped 300 that year, making this the world’s fastest couple, a distinction that still stands.
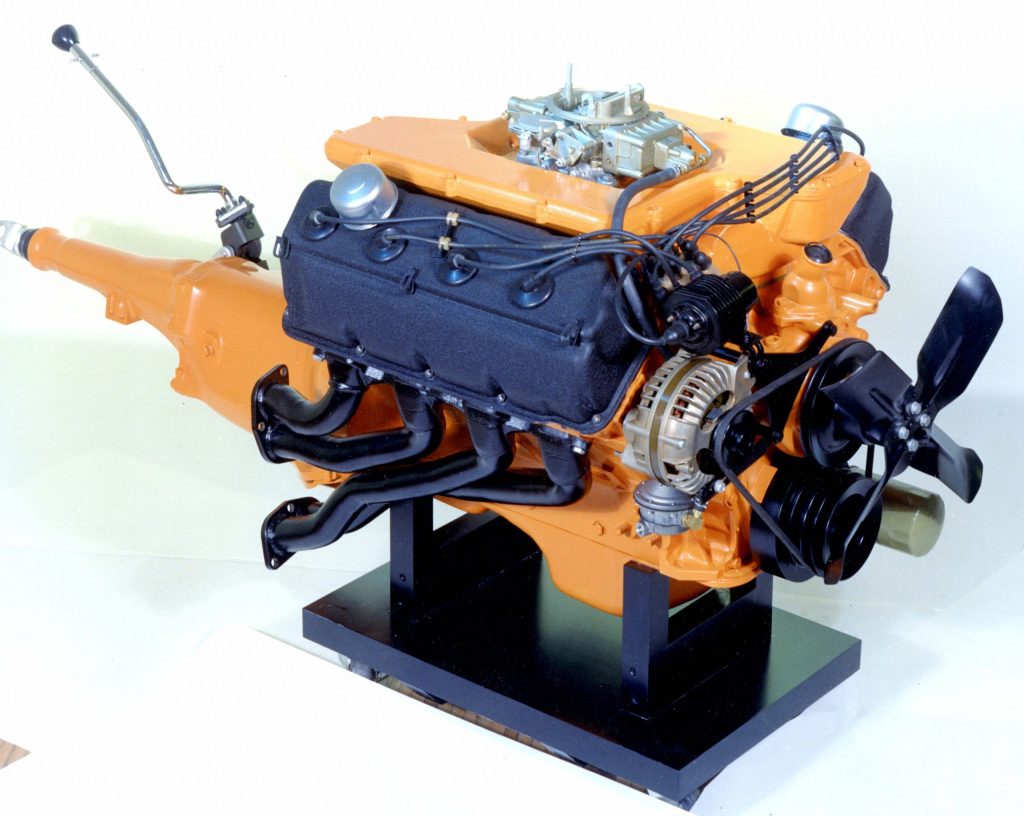

1966: The Street Hemi 426 V8 arrives in Plymouth and Dodge showrooms, producing 425 horsepower.
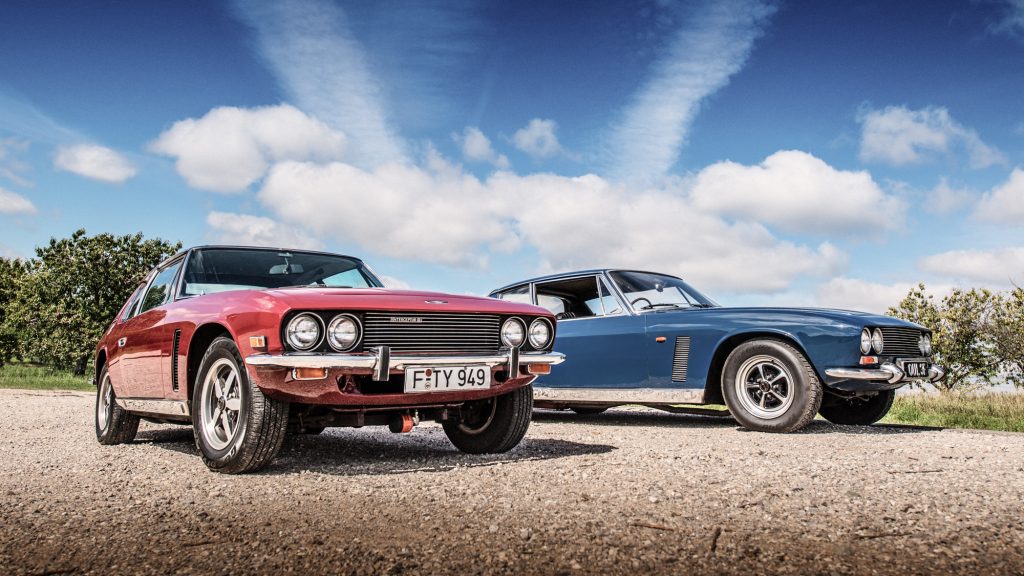

The Jensen Interceptor is the first performance car with all-wheel drive and anti-lock brakes.

1967: Following thorough chassis upgrades, Carroll Shelby installs 7-litre Ford big-block V8s in his Cobras, upping output to 425–485 horsepower.

Firestone introduces low-profile Wide Oval bias-ply tires.
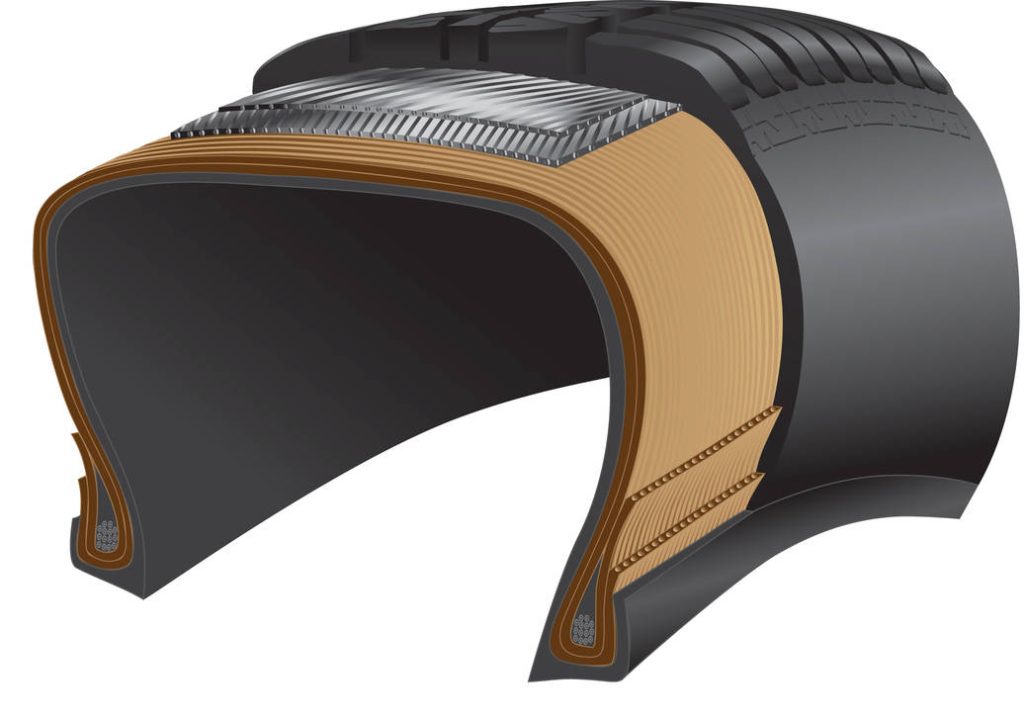

1968: Consumer Reports touts the advantages of radial tires.

1971: Buick introduces a technology to help drivers get horsepower to the pavement: electronic traction control.

1973: Horsepower ratings switch from gross to net figures. The gross procedure included no mufflers or engine-driven accessories, whereas net ratings are a more accurate assessment of the engine as installed in the car. The rating for Corvette’s 5.7-litre V8 drops from 270 to 200 horsepower.

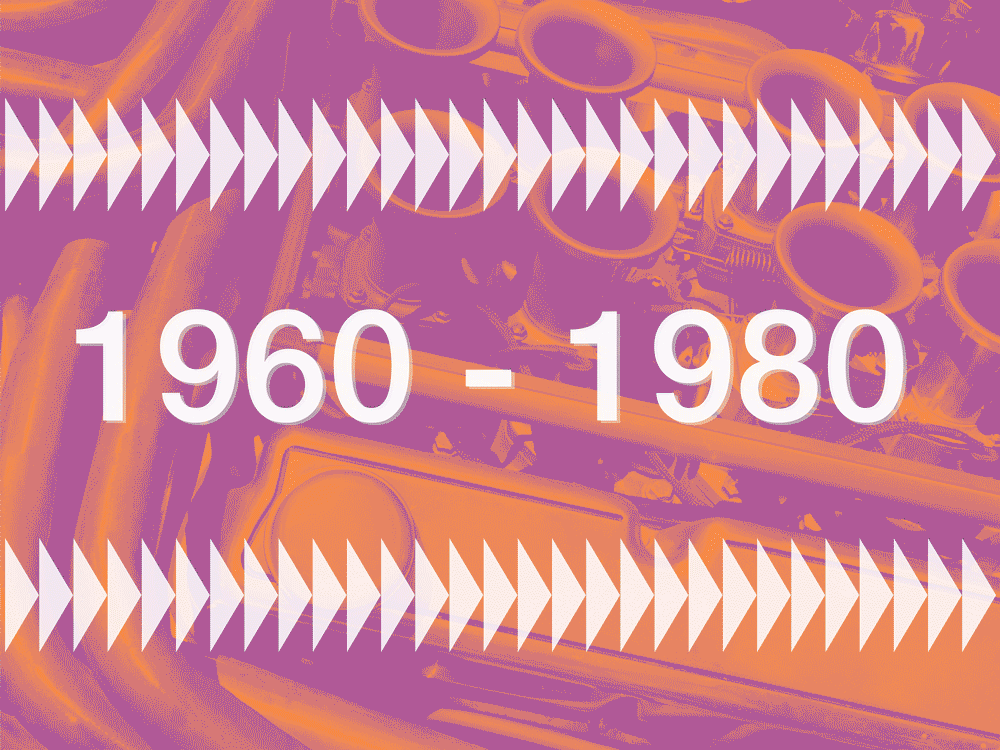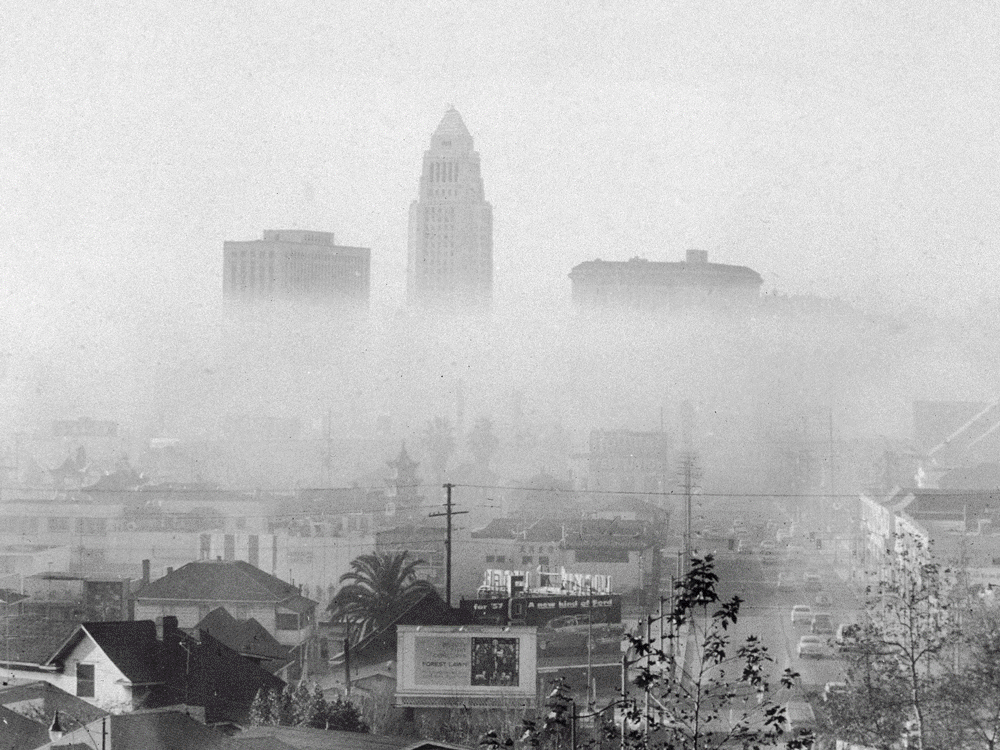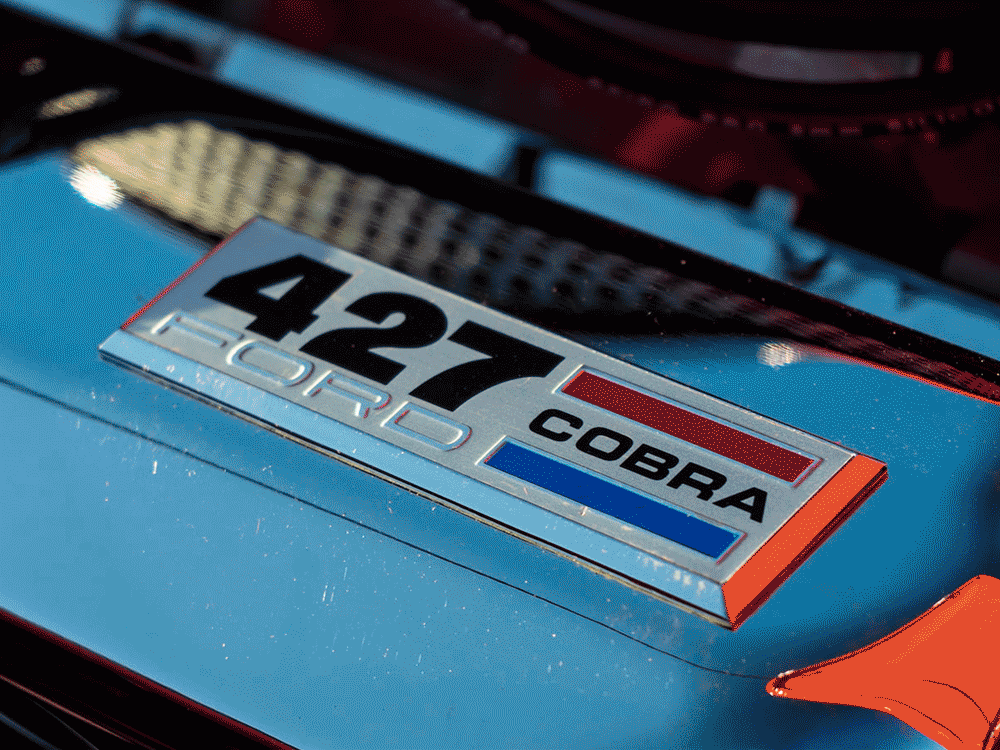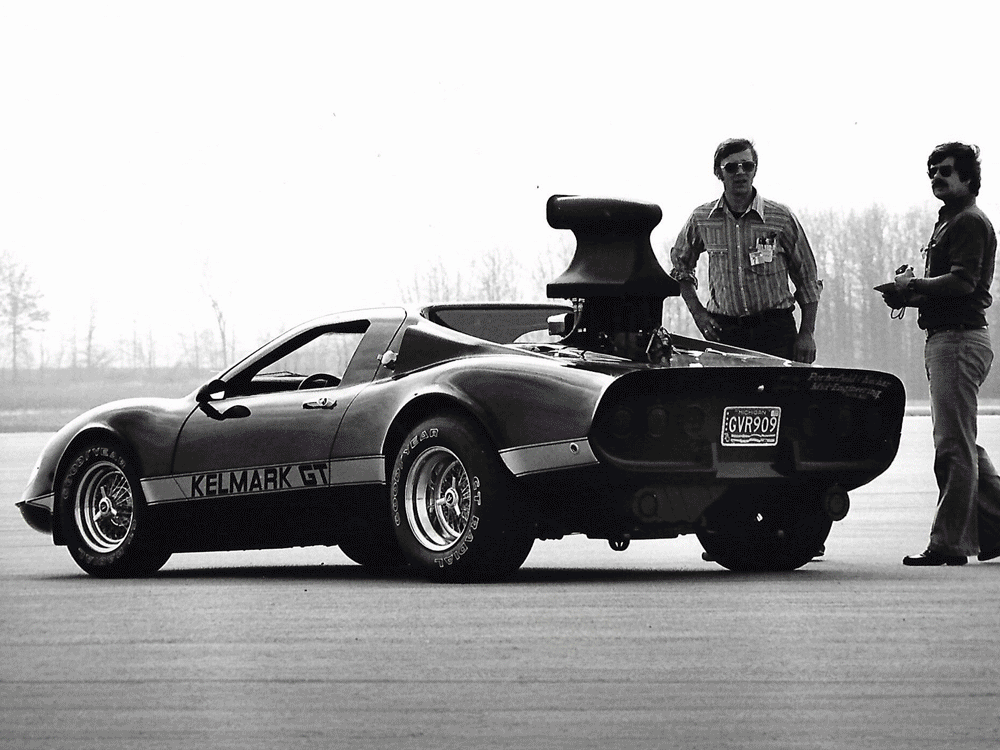
1975: Catalytic converters begin restricting exhaust systems. These devices are fouled by lead in gasoline, so the US Environmental Protection Agency begins restricting the amount of this octane-boosting additive.

It’s not all bad news: Porsche introduces the 911 Turbo, initially rated at 260 horsepower.

1976: Italian tire manufacturer Pirelli introduces low-profile P7 radials.
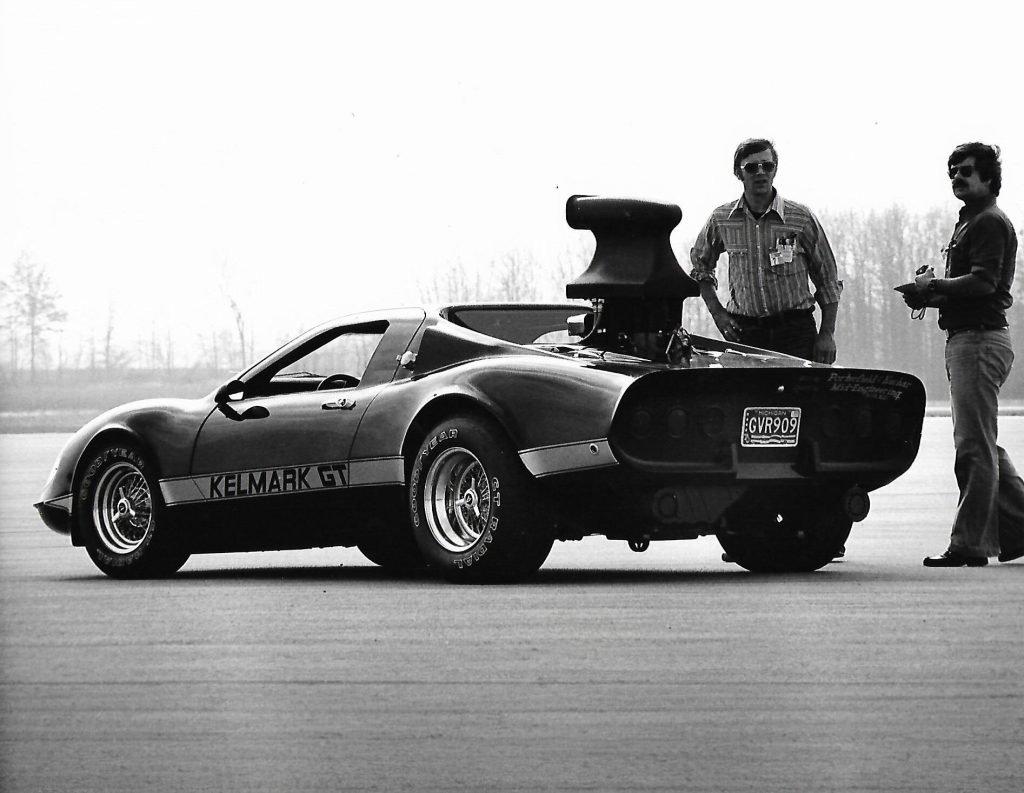

1978: With manufacturers focused on fuel economy, tuners attempt to fill the void. GM engineer Bill Porterfield offers Car and Driver magazine editor Don Sherman (your narrator) a drive in his Kelmark GT, a fiberglass copy of a Ferrari Dino armed with a 737bhp Chevy big-block V8. At Ohio’s Transportation Research Center, with one hand holding a toggle switch up to engage an auxiliary fuel pump, the Kelmark hits 202.7mph.
Return to Part IV (1950–1960), and stay tuned for Part VI (1980–2000).